Description
Sweet Pea Heirloom Seed Mix - Classic Charm, Fragrant Blooms
For the past few years, long-time customers would share nostalgic memories, asking if we knew where to find those old-fashioned Sweet Peas – the ones whose intoxicating perfume greeted you halfway down the garden path, just like at their grandparents' house. They had tried modern varieties, they told us, appreciating the big flowers but always missing that legendary scent. We understood completely, but finding seeds reliably delivering that classic fragrance proved elusive until a visit to one of our flower growers' field trials.
Walking the rows, we kept catching an extraordinary aroma – elusive hints of warm honey and oranges. Intrigued, we put down our notebooks and literally followed our noses upwind, the scent growing stronger until we arrived at a stunning bed of multi-colored Sweet Peas, radiating the exact, almost intoxicating perfume our customers cherished! We knew then that we had found the fragrant heirloom Sweet Pea (Lathyrus odoratus) experience our customers were seeking, capable of bringing that truly unforgettable scent back to gardens.
Details
The Sweet Pea holds a cherished place in the hearts of gardeners worldwide. Esteemed for its range of colors and intoxicating fragrance, this climbing annual vine brings vertical interest and a touch of old-fashioned charm to gardens. It is a member of the Legume or Pea family, grown as a cool-season annual that completes its life cycle in one season and should not be confused with its unscented perennial relative, the Everlasting Pea. While commonly called Sweet Pea, it's sometimes specified as Annual Sweet Pea.
This variety features vigorous climbing vines reaching 3 to 8 feet tall or more, using branched tendrils at the leaf tips to actively twine around and ascend supports. Plants generally spread between 1 and 3 feet wide. Their slender stems are distinctively winged, bearing compound leaves with usually one pair of oval or elliptic green leaflets.
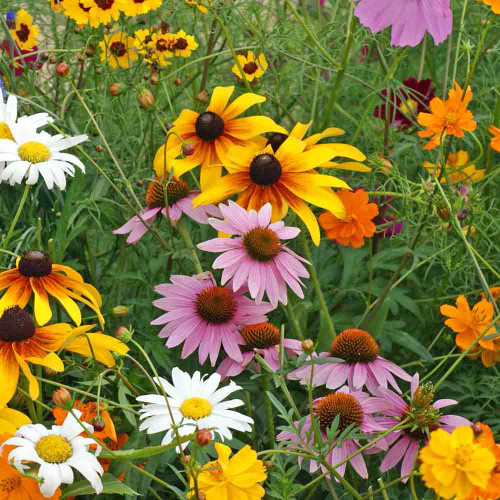
The iconic flowers display the classic butterfly-like structure, borne in clusters. The colors include a beautiful spectrum of lavender, pink, purple, red, salmon, and white, perfect for creating an old-fashioned and aromatic garden display. Flower size generally ranges from 1 to 3 inches across. A key trait is fragrance; older heirloom 'Grandiflora' types generally possess the strongest, most intoxicating perfume (often described as intense, sweet, or reminiscent of honey and orange blossoms), while many modern hybrids bred for larger flowers may have a less pronounced scent. After flowering, flattened, often hairy pods form, containing small, round seeds. Sweet Peas are grown as annuals across USDA Zones 2-11, depending on planting time. Seedlings exhibit good frost tolerance, and the time from direct sowing to first flowers is typically 75-90 days.
History
The Sweet Pea's journey from a wild Sicilian flower to a global garden favorite is a story intertwined with monks, botanists, and dedicated breeders. Native to the Mediterranean region, specifically Southern Italy including Sicily, its formal discovery is credited to Francisco Cupani, a Franciscan monk, around 1695. He sent seeds of the fragrant wild pea to Holland and England. Introduced to northern Europe, its development accelerated dramatically in the late 1800s thanks to Scottish breeder Henry Eckford, the "Father of the Sweet Pea." His work created the 'Grandiflora' type, expanding the color range and flower size while retaining the powerful fragrance heirloom lovers seek. Sweet Peas also played a role in early genetic science, used by researchers like Reginald Punnett to study trait inheritance.
Uses
Prized for their captivating fragrance and old-fashioned visual charm, climbing Sweet Peas transform fences, trellises, and arbors into stunning vertical displays of color and scent in the garden. They are also highly prized as cut flowers, bringing beauty and scent indoors. For the longest vase life (typically 4-6 days), harvest stems when the top 2-3 buds are still unopened, cut them in the cool morning, and immediately place them in water with flower preservative, keeping bouquets away from ripening fruit (ethylene sensitivity). Furthermore, Sweet Pea flowers are a valuable resource for pollinators, visited by various bees (honey, bumble, carpenter, mason, leaf-cutter) and butterflies, contributing to garden health.
Companion Planting
As legumes, Sweet Peas contribute beneficial nitrogen fixation to the soil via root nodules, potentially enriching the soil for nearby nitrogen-hungry plants like corn or leafy greens. Their perfumed flowers also help attract pollinators useful for other garden crops. Planting low-growing annuals at their base can help keep Sweet Pea roots cool and shaded.
Avoid planting Sweet Peas directly next to Alliums (onions, garlic) or Fennel, as these are traditionally thought to inhibit legume growth. Ensure good air circulation between plants.
Planting and Growing Tips
Success with Sweet Peas hinges on planting them during periods of low temperatures they prefer, as they falter in intense heat. In mild-winter climates (Zone 8+), the ideal time to direct sow seeds is typically in the fall (October-November) for early spring blooms. Colder areas (Zone 7 and below) are best suited to direct sowing outdoors very early in spring as soon as the soil is workable (seedlings tolerate light frost).
Because Sweet Pea seeds have a hard coat, nicking the seed coat gently or soaking seeds overnight is highly recommended to improve germination. Sow seeds about 1/2 to 1 inch deep (as they need darkness to sprout) and space climbing varieties about 6-8 inches apart. Cool germination temperatures between 50-65°F (10-18°C) are ideal; expect sprouts in 7-21 days.
Choose a planting site that receives full sun (at least 6 hours daily), providing afternoon shade only in very hot summer regions. They demand rich, fertile, well-drained soil, ideally neutral to slightly alkaline. Amend generously with compost. Critically, install sturdy support (at least 6 ft tall) like trellises or netting at planting time.
Water consistently throughout the growing season, especially during flowering, aiming for deep soakings at the soil level. Feed regularly during active growth with a low-nitrogen, high-potassium/phosphorus fertilizer (like tomato fertilizer) to encourage abundant blooms rather than excessive leafy growth. Pinch out the central growing tip of seedlings when 4-6 inches tall for bushier plants. Keep weeded, especially when young, and apply organic mulch to help conserve moisture and keep roots cool. Furthermore, Sweet Peas are generally considered resistant to browsing by deer and rabbits.
Harvesting Tips
Sweet Peas make wonderful, although relatively short-lived, cut flowers, bringing their fragrance indoors. For the longest vase life, typically around 4 to 6 days, harvest stems in the cool of the early morning when at least two or three buds at the very tip of the flower spike remain unopened. Use clean, sharp scissors or snips and place stems immediately into cool water with preservative. Keep bouquets away from ripening fruit.
Beyond enjoying bouquets, frequent cutting or deadheading is absolutely essential to keep your Sweet Pea vines blooming profusely throughout their cool season. As an annual, the plant's primary goal is to set seed; letting pods develop signals flowering to stop. By regularly removing spent flowers before seed pods form, you encourage the plant to produce more blooms – the more you pick, the more flowers you'll get!
Caution: Ornamental Sweet Pea - Not Edible. While related to edible peas, Sweet Peas (Lathyrus odoratus) are poisonous if ingested. All parts of the plant, especially the seeds, contain toxins harmful to humans and pets if ingested. Crucially, do not confuse these with edible garden peas (Pisum sativum). Handle seeds responsibly and keep plants away from children and pets. When grown solely for their beautiful flowers and lovely scent, and sensible precautions are taken against ingestion, Sweet Peas remain a cherished and rewarding addition to the garden.
Learn More
From the soil to the seed to the food you eat - we'll help you grow your best garden!