Description
Dwarf Sugar Pea - Melting Sugar Flavor
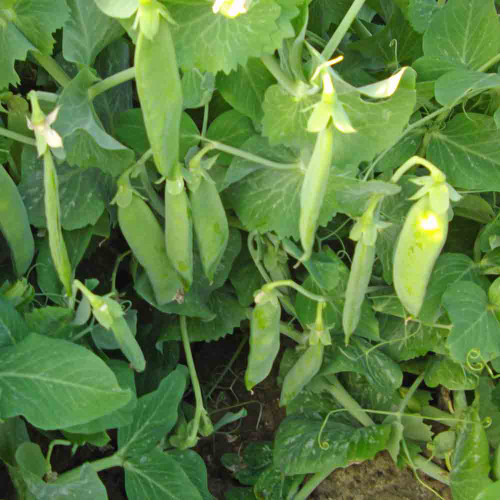
The Dwarf Sugar Pea hides a delightful secret: While most gardeners know of its legendary sweet, tender pods with a flavor often described as "melting sugar," this compact variety offers a versatile ingredient that will inspire your creativity, giving you even more reasons to add this delightful pea to your garden. Beyond those delectable pods, you'll discover vibrant blossoms perfect for garnishing and delicate shoots ideal for salads and stir-fries.
This heirloom variety, a favorite since 1773, is also incredibly versatile in the garden. Think beyond just peas in a pod with this container-friendly variety that transforms any sunny spot into a productive pea patch. The pods grow in clusters at the top of the plant, making them easy to spot and pick. Not only does it mature early for a spring harvest, but it can also be planted in late summer for a fall crop, giving you a longer supply of sweet, tender pods.
Details
The Dwarf Sugar Pea is a charmingly compact plant, well-suited for smaller gardens or containers, so even if your gardening space is limited to a balcony or patio, this container-friendly variety allows you to grow fresh peas wherever you choose. Typically reaching 28 to 36 inches, it can surprise you with its vigor, occasionally stretching to 4 or 5 feet under ideal conditions, rewarding you with a plentiful harvest. Its delicate leaves, arranged in a feather-like pattern along either side of a central stem—a formation known as "pinnate"—create a lush backdrop for the eye-catching blossoms. The bi-colored flowers, a striking combination of deep purple and soft pinkish-white, add a touch of elegance to the garden. These blossoms are not just ornamental; they are also edible, offering a mild, pea-like flavor. They also add a touch of beauty to your garden, attracting pollinators and creating a vibrant display.
As the blossoms fade, they give way to the main attraction: the 2 to 3-inch pods, flat and fleshy, and a vibrant green. Their smooth texture hints at the sweet, tender peas within. The peas themselves are small and tender, with a sweet and delicate flavor that has been described as "melting sugar." The pods grow in close-knit clusters, their abundance promising a generous harvest for you and your table.
This variety thrives in full sun to partial shade and prefers cool weather, making it an excellent choice for both spring and fall gardens. Its hardiness across USDA zones 3 through 9 makes it a reliable choice for gardeners in various climates. It can be planted as soon as the soil can be worked in the spring, even before the last frost, offering an early taste of spring's bounty. And as the heat of summer fades, you can sow another crop, enjoying its continued production as the weather cools off, extending the season for these delectable peas.
Well-drained soil is crucial for successful cultivation. Sandy soils are ideal, but any soil with good drainage will suffice. Consistent moisture is essential, especially during germination and flowering. Water regularly, aiming for about an inch of water per week if rainfall is insufficient. Using a soaker hose or drip irrigation system can help maintain consistent moisture levels and prevent the foliage from getting wet, which can encourage disease.
Types of Fresh Peas
- Snap Peas: Eaten whole, pod and all. Crisp, sweet, and stringless. Snap peas differ from shelling and snow peas in that their pods are thicker, rounder, crunchier, juicy, sweet, and entirely edible apart from the string.
- Sugar Peas: Similar to snap peas, but with flatter pods and slightly smaller peas. Also, eaten whole.
- Shelling Peas: Grown for the peas inside the pod, which are shelled and eaten fresh, frozen, or canned.
- Edible Pod Peas: A broader category encompassing both snap and sugar peas.
History
The story of peas begins in Middle Asia, over 5,000 years ago, where archaeological evidence reveals their presence in ancient settlements, showing their importance as a dependable source of food. From there, they journeyed across continents, reaching the Near East and Ethiopia, their cultivation spreading like wildfire. By the Middle Ages, peas were a staple in Northern Europe, enjoyed by people from all walks of life. Their sweet flavor and versatility made them a favorite among farmers and gardeners alike, offering a fresh taste and a welcome change of pace from the limited diets of the time.
The development of edible-podded peas—snow peas with their flat, tender pods, and snap peas with their thick, sweet pods—marked a turning point in pea history. These varieties, bred from careful selection and a keen eye for desirable traits, revolutionized how we eat peas.
From this rich history emerges the Dwarf Sugar Pea, with its compact, bushy growth and sugary-sweet flavor. Dating back to at least 1773, it was likely the variety described as the "Early Dwarf Dutch Sugar pea" in Fearing Burr's 1863 book Field and Garden Vegetables of North America, proof that some things, like a truly delicious pea, never go out of style. It's believed that Dutch and French horticulturists, pioneers in developing cold-tolerant, early-maturing peas, played a crucial role in refining this variety. The Netherlands’ maritime climate and France’s rich horticultural tradition made them hubs for pea innovation, fostering an environment where such a treasure could be nurtured and shared.
Gardeners have cherished this old heirloom for centuries, its seeds carefully preserved and passed down through generations. In 1892, D.M Ferry and Company introduced it to a wider audience, offering its seeds commercially and introducing it to home gardeners, who have grown and enjoyed it ever since.
Uses
This versatile pea offers more than just sweet pods. The edible flowers and tender shoots add a unique touch to salads and garnishes, extending your enjoyment of this plant beyond the pea itself.
Fresh from the Vine: Step into your garden and pluck a Dwarf Sugar Pea pod at its peak. Savor the crispness and sweetness that melts in your mouth like a sugary treat, a delightful reward for your gardening efforts.
Salad Symphony: Toss a handful of Dwarf Sugar Pea pods and blossoms into your salad for a burst of color, texture, and flavor. The sweet pods and delicate flowers create a delightful symphony of tastes, complementing a variety of greens, fruits, and cheeses.
Stir-Fry Sensation: Add Dwarf Sugar Pea pods to your stir-fry for a touch of sweetness and crunch. Their quick cooking time ensures they retain their vibrant color and crisp texture, adding a delightful contrast to savory sauces and spices. Toss in a few of the tender shoots for an added layer of flavor and visual appeal.
Try braising the pods alongside poultry or shrimp, allowing their sweetness to complement the richness of the meat. They also pair beautifully with a variety of flavors, from the subtle heat of chiles to the bright zest of lemon and the earthy aroma of mushrooms.
Companion Planting
Companion planting, strategically combining different plants in your garden, can significantly benefit your Dwarf Sugar Peas. This practice not only maximizes space and resources but also helps attract beneficial insects and improve soil health. With their climbing nature, these peas will readily latch onto cornstalks as a natural trellis, their delicate tendrils intertwining for support. In return, the peas enrich the soil with nitrogen, a valuable nutrient for corn and neighboring plants.
Root vegetables, such as carrots and radishes, are also excellent companions. Their growth aerates the soil, creating a welcoming environment for the pea's roots to spread and flourish. Marigold blossoms serve a dual purpose, adding a cheerful splash of color while deterring pests with their distinctive scent. Similarly, the cheerful blooms of nasturtiums act as a trap crop, luring aphids away from your peas.
While many plants thrive alongside peas, it's best to avoid planting them near allium family members, such as onions, garlic, and chives. These vegetables can sometimes inhibit the growth of peas, so it's best to keep them at a distance.
Planting and Growing Tips
Early Spring Planting: Sow your Dwarf Sugar Pea seeds as soon as the soil can be worked, even before the last frost has faded. These hardy peas relish cool weather, making them a perfect choice for an early spring planting.
Late Summer Planting: Extend your pea season with a late summer sowing. As the heat of summer wanes, the Dwarf Sugar Pea will thrive in the cooler temperatures, providing a second harvest of sweet, tender pods just as the fall season arrives.
Ensure the soil is well-drained and fertile, amending with compost or well-rotted manure if needed. Sow seeds 1 inch deep and 1 to 2 inches apart. The optimal soil temperature range for germination is 50-75°F, so a bit of patience may be needed in colder climates.
This variety is known for its resilience, tolerance to short hot spells well and resistance to common pea diseases like powdery mildew, ensuring a healthy and abundant harvest. Providing a trellis or other structure for them to climb increases yields and makes harvesting easier.
Full sun (at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily) is ideal for optimal growth and pod production. In warmer climates, providing some afternoon shade can help prevent the plants from bolting (flowering prematurely) in hot weather. Consistent moisture is crucial, especially during flowering and pod development. The soil should be kept moist but not waterlogged. Mulching around the plants can help conserve moisture and suppress weeds.
Peas generally don't require heavy fertilization, especially if the soil is amended with compost.
Harvest Tips
Dwarf Sugar Peas are typically ready for harvest about 65 days after planting. Regular harvesting encourages continued production, so check your plants every few days. The pods grow in clusters, making them easy to spot and harvest, ensuring you don't miss a single sweet treat. Pick the pods when they are plump and well-filled, but still tender. Harvesting in the morning, while the pods are cool, ensures the best flavor and texture.
The best way to determine if your sugar peas are ready to pick is to taste them! Sample a few pods as they begin filling out, and you'll quickly get a sense of when they're at their peak flavor and tenderness.
Learn More
From the soil to the seed to the food you eat - we'll help you grow your best garden!
1 Review
-
Compact plant with very attractive flowers
Good germination, compact plant with very attractive flowers, heavy production of very small pea pods. Plants did not stand up well to the onset of hot weather.